Article featured in Oilfield Technology's 2022 summer magazine (pages 42-45)
As the global energy mix transitions to low-carbon sources, there may be fewer opportunities for new oil and gas field developments. As a result, many operators will shift their focus towards recovering more from existing reservoirs, and this strategy includes improving the management and performance of their Horizontal wells.
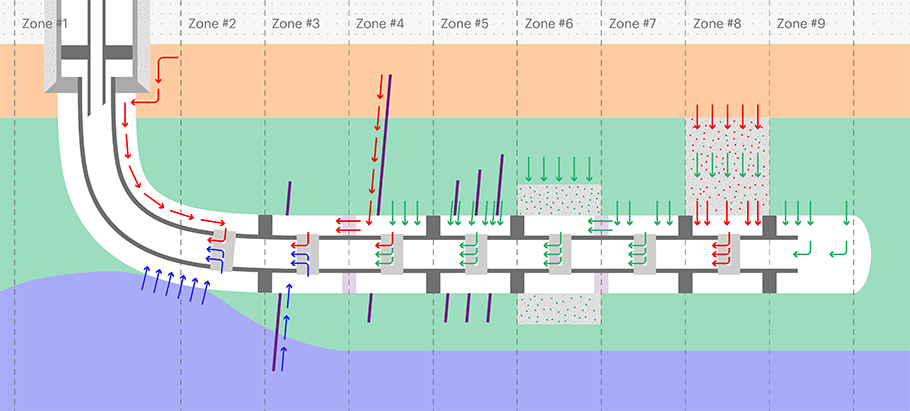
Horizontal wells generally deliver much higher levels of productivity than their vertical counterparts, but this performance can often come at a cost. Understanding the interactions between a horizontal well and the reservoir can be extremely challenging. The combination of variable well angles, extended reservoir contacts, the presence of fluid mixtures and segregated flows, formation changes, fractures and intricate completions presents a formidable challenge for analysis using conventional production-logging tools (Figure 1).
Standard production-logging technology may, under some conditions, be able to map the multiphase flows encountered in a horizontal wellbore, but it cannot quantify flows for fluids exiting or entering the reservoir behind the completion. This means that wellbore production logs do not provide a complete picture of flow dynamics across the well system. Asset teams that base development, production or remediation plans on an incomplete partial flow diagnosis may be risking lower productivity, reduced asset performance, and higher carbon overhead.
A new beginning
Reservoir and production engineers have been looking to overcome the drawbacks of conventional production surveys in horizontal wells for many years. Their key requirement has been a system that could deliver continuous flow profiles across different completion and reservoir scenarios, and would also be effective in reservoirs with fractured formations.
TGT Diagnostics has been working on addressing these needs for several years and, in February 2022, launched the Horizontal Flow diagnostics product with Cascade3 technology. Specifically designed for horizontal wells, this system offers more realistic flow modelling and accurate continuous flow profiles in a wide variety of completion and reservoir settings. The insights gained from this have the potential to help companies reduce operating costs and energy consumption while increasing ultimate recovery.
The new technology uses an advanced modelling simulation engine to predict the hydrodynamic and thermodynamic behaviour of fluids and their surroundings as they flow through the well-reservoir system. This translates temperature, pressure and other well-system data into continuous reservoir flow profiles. These profiles deliver a true picture of inflow and outflow, and this is the case even for challenging wells and those that feature natural or hydraulically induced fractures.
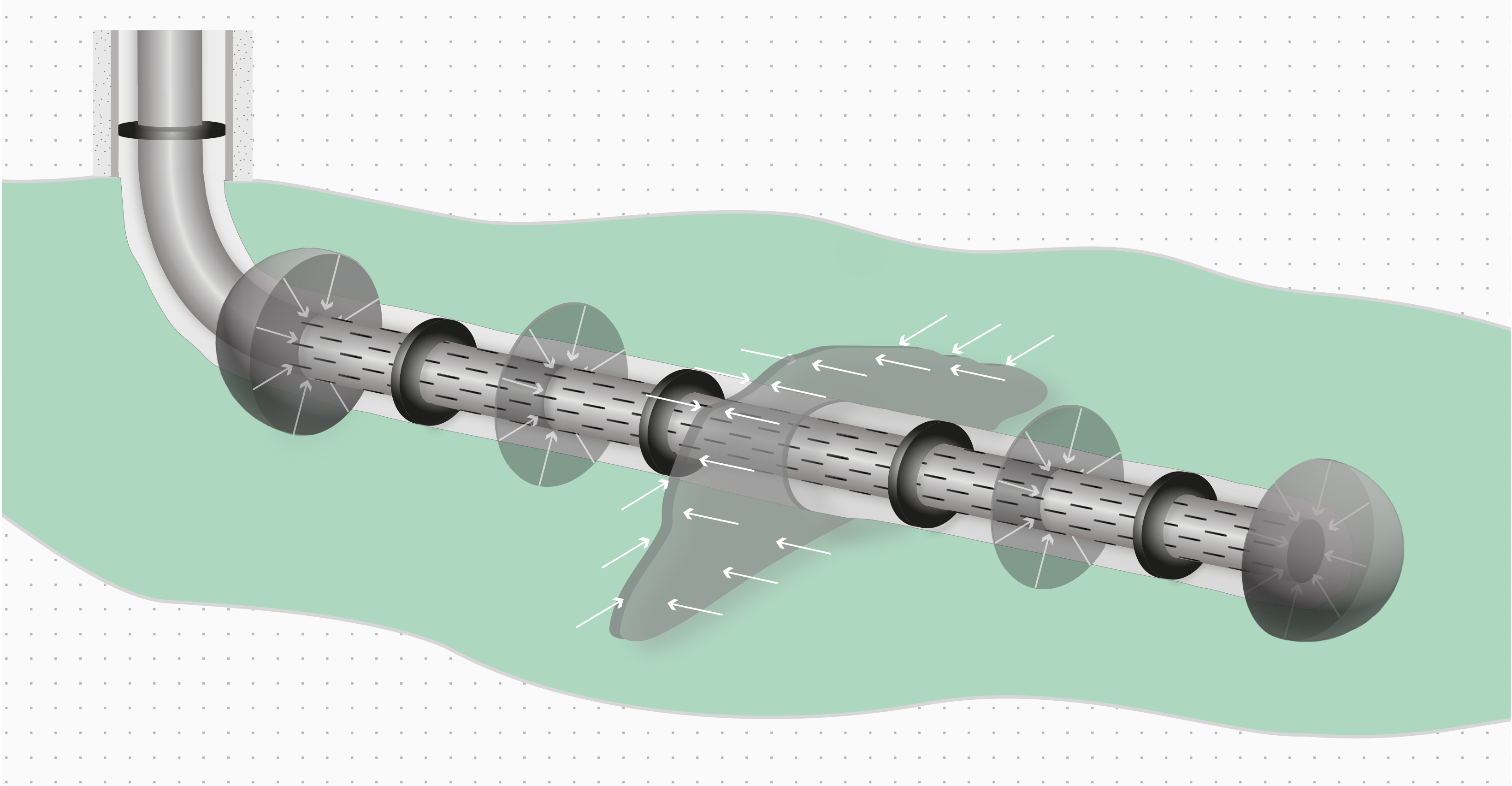
The ability to assess flow in fractured reservoirs is important because, although fractures can boost hydrocarbon production, they can also provide pathways for early water or gas breakthrough. The new diagnostics technology can evaluate the radial, spherical and linear/fracture flow patterns commonly encountered in horizontal well systems (Figure 2). This provides an accurate assessment of linear flow occurring in the fractures and makes it possible to determine the fracture contribution. This is particularly useful when combined with the Chorus acoustic sensing system that identifies fracture locations along the wellbore.
Applications and benefits
Operating companies want to maximise hydrocarbon recovery in the safest, cleanest and most economical way possible. Having an accurate picture of fluid flow in the wellbore and the immediately surrounding reservoir rock gives asset teams greater confidence in their decisions and makes it easier to enhance production, maximise recovery and rectify well problems.
The new diagnostics system provides useful input in key areas such as reservoir, well and resource management, and can even help companies enhance their environmental performance and reduce the carbon footprint of production operations.
Insights for reservoir management
Effective reservoir management is a key objective for oil and gas operating companies. The development of any hydrocarbon reservoir disturbs a natural balance of rocks and fluids that may have existed for millions of years. Understanding how a reservoir will behave as new wells are drilled and fluids are extracted or injected is a daunting task. Reservoir engineers deal with huge uncertainties in their quest to maximise hydrocarbon recovery, reduce operating costs and extend the economic life of the reservoir.
At the heart of the reservoir-management process is the dynamic reservoir model, which provides a basis for all field development and hydrocarbon recovery decisions, infrastructure investments and reserves estimations. The robustness and accuracy of the model is critical to successful reservoir management, and any inaccuracies may lead to poor decisions and substantial losses.
As more data is collected, the dynamic reservoir model is updated by the reservoir engineering team using a process known as history matching. Insights from this new diagnostic system can play a critical role in history-matching, thus helping to reduce the uncertainty envelope and improve the model. A continuous flow profile provides a clear and direct quantification of the flow performance of the reservoir as it feeds the well system. In contrast to standard wellbore production surveys, which can be hindered by completion or reservoir integrity issues, Horizontal Flow can deliver a true flow profile. The continuous nature and sensitivity to low flow rates help provide a more accurate measurement of effective pay length, a key metric for making production forecasts and reserves estimates.
The new system is also effective in the presence of fractures. Predicting and preventing water or gas breakthrough is one of the most important and challenging tasks faced by reservoir engineers. Having a deeper understanding of downhole flow dynamics can help provide an early warning of locations where water or unwanted gas may be reaching the well.
The new workflow can also be used to estimate or validate other key parameters such as reservoir pressure, permeability and skin factor. This independent verification can help reservoir engineers to resolve uncertainties, improve history matching and optimise the dynamic reservoir model.