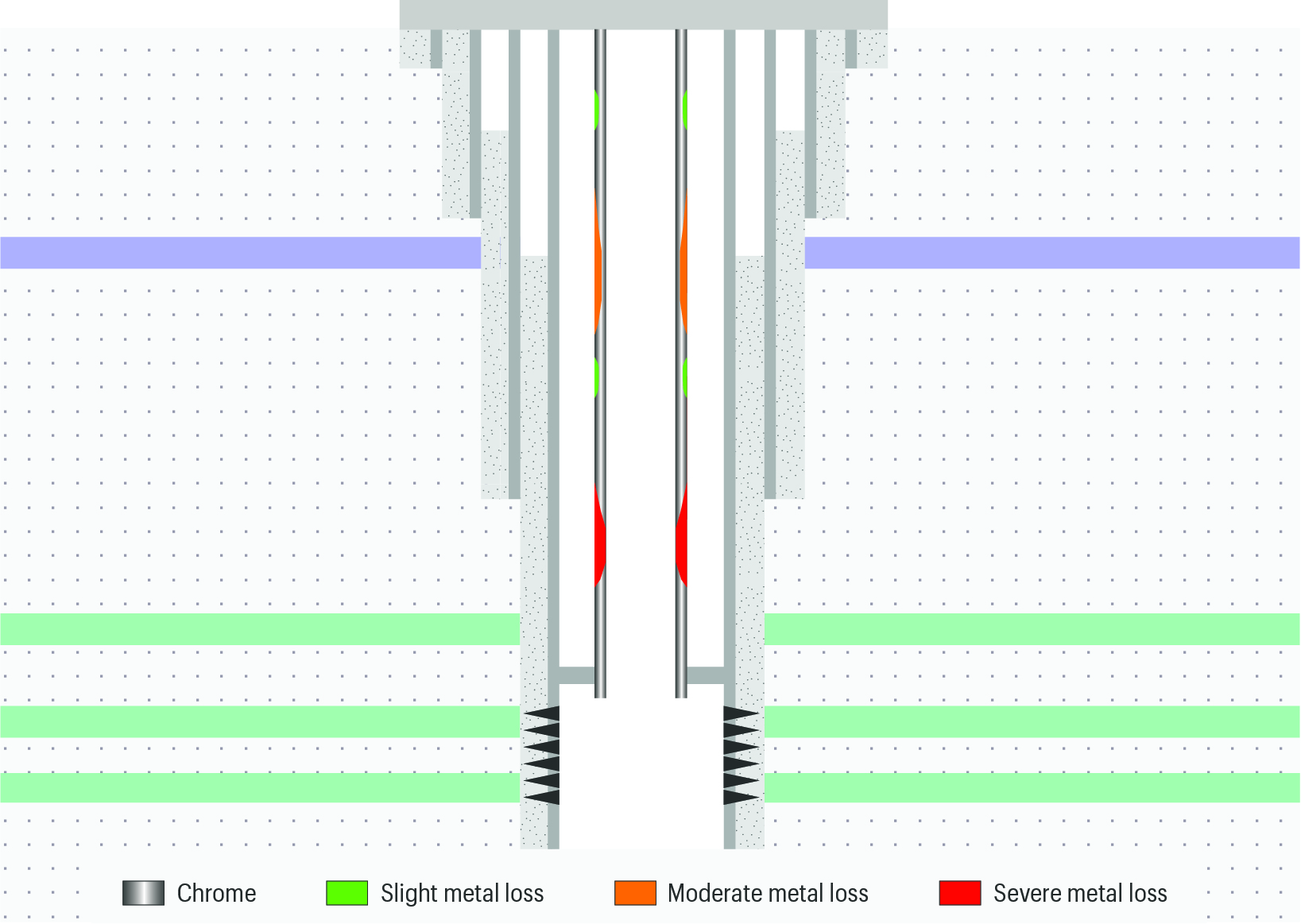
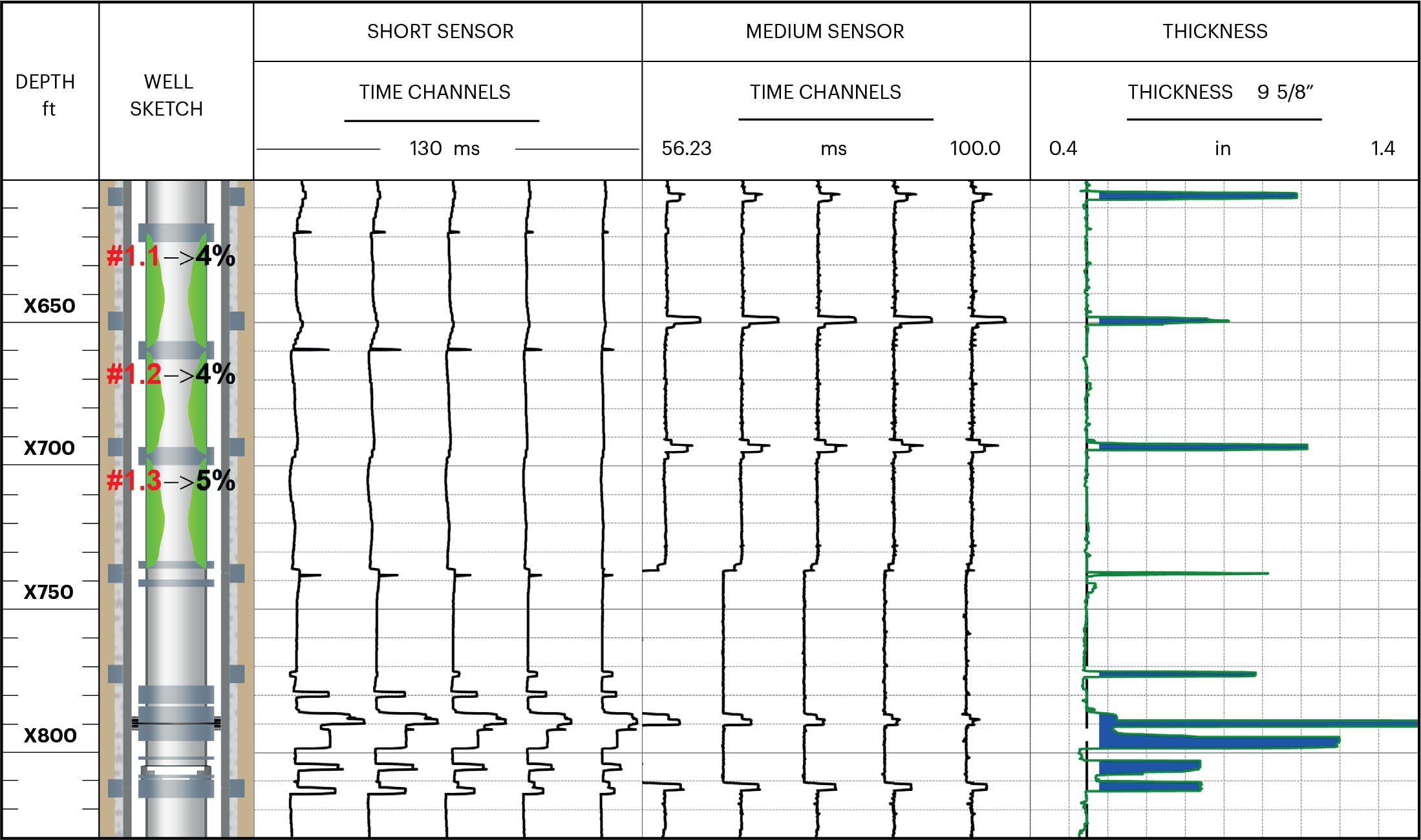
Using corrosion-resistant materials such as high-chromium–nickel alloy for tubulars helps to protect well completions from corrosive fluids. But these alloys present a serious challenge for conventional electromagnetic pipe inspection systems.
This ADNOC survey took place in a high-temperature sour well. The flow-wetted areas of the well had been completed with chrome-resistant alloy (CRA) tubulars. The diagnostic system, particularly the data acquisition and interpretation process required for the corrosion assessment of CRA tubulars, is much more complex than for conventional steel tubulars. In this case, the corrosion study was a high-temperature environment where the produced gas contained hydrogen sulphide (30%) and carbon dioxide (10%).